Unlock Hydropower’s Green Revolution
Unlock Hydropower’s Green Revolution
Hydropower, one of the oldest sources of renewable energy, is experiencing a resurgence as the world seeks sustainable and clean energy solutions. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of hydropower, its benefits, challenges, and future trends. Furthermore, read more about Introduction to Hydropower for a comprehensive understanding.
Understanding Hydropower
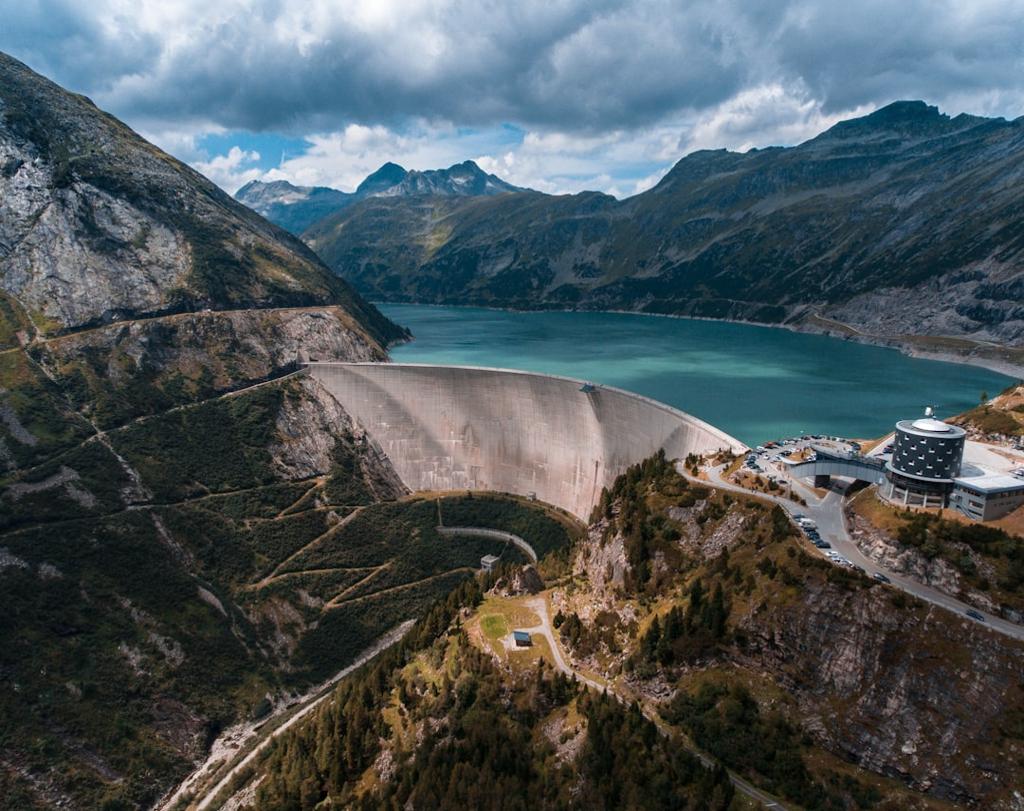
Hydropower, or hydroelectric power, is energy derived from the force of moving water. It’s a form of renewable energy that harnesses the natural flow of water to generate electricity. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), hydropower is the world’s largest source of renewable electricity, contributing about 16% of global electricity generation.
Benefits of Hydropower
Hydropower offers several advantages that make it an attractive option for sustainable energy production. Consequently, according to a study by the U.S. Department of Energy, the benefits are substantial. However, the advantages can be broadly classified into three categories: environmental, economic, and social.
Environmental Benefits
Specifically, hydropower produces no direct waste and has a significantly lower output of greenhouse gases than fossil fuel energy sources, making it a cleaner, greener alternative. Furthermore, it helps in reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change.
Economic Benefits
Hydropower plants have long lifespans and low operation and maintenance costs, leading to stable, low-cost electricity supply. Moreover, they contribute to the local economy by creating jobs and stimulating regional development.
Social Benefits
Hydropower plants often lead to the creation of reservoirs, providing opportunities for water supply, irrigation, and recreational activities. Additionally, they play a crucial role in managing water resources and flood control.
Challenges and Solutions for Hydropower
Despite its numerous benefits, hydropower also faces several challenges. These include environmental and social impacts, high upfront costs, and regulatory hurdles. However, with innovative technologies and sustainable practices, these challenges can be addressed. For instance, for more details, see Challenges of Hydropower.
How Hydropower Works: A Closer Look
Hydropower plants convert the kinetic energy of flowing or falling water into mechanical energy, which is then transformed into electrical energy. This process involves a series of steps, including dam construction, water storage, and electricity generation. As an example, an external resource is Wikipedia’s page on Hydropower.
Future Trends in Hydropower
The future of hydropower looks promising with advancements in technology and increased focus on sustainability. Trends like small-scale hydropower, pumped storage, and integration with other renewables are shaping the future of this sector. Similarly, explore the future trends to understand how hydropower is evolving.
Conclusion: Embracing Hydropower
In short, hydropower offers a sustainable solution to meet our growing energy needs while mitigating environmental impacts. Despite the challenges, with proper planning, innovative technologies, and sustainable practices, hydropower can play a pivotal role in the global energy mix. Therefore, embracing hydropower is not just an option, but a necessity for a sustainable future. Altogether, the green revolution of hydropower is here to stay.
References
– International Energy Agency (IEA) – Hydropower
– U.S. Department of Energy – Hydropower Vision
– Wikipedia – Hydropower
– Internal: Introduction to Hydropower
– Internal: Challenges of Hydropower
– Internal: Future of Hydropower









Post Comment